| Acoustics of the clarinet |
Bb clarinet |
E3 |
|
Fingering Acoustic schematic Non-specialist introduction
to acoustic impedance Notes are the written pitch. |
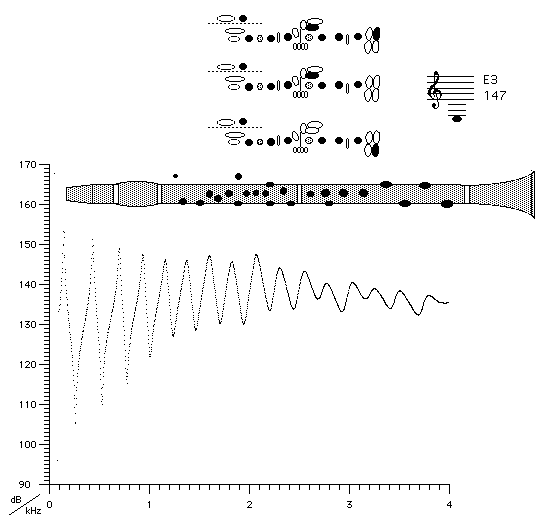
This is the lowest note on this clarinet. All tone holes are closed, so the clarinet most closely resembles a cylindrical, closed pipe (For a detailed explanation see The clarinet as a closed pipe). As a result, the regular series of maxima (and minima) in Z(f) extends to high frequencies. The maxima (and minima) become weaker at high frequencies for several reasons: first, the loss of energy where the moving air is close to the walls is more important at high frequency. Second, the bell radiates high frequencies better than low, so there is less reflection of high frequencies and so weaker resonances. Third, the effect of the springiness of the reed is to reduce the resonances at high frequencies (its compliance, to be technical) (which is why softer reeds don't play the high notes as well). The first several maxima can be played. See also flutes and clarinets for a discussion of details of the impedance curve of a cylindrical tube.
To understand how the bell and the mouthpiece contribute to the shape of this curve, see frequency response and acoustic impedance of clarinets.
In the sound spectrum below, note that the odd harmonics are stronger than the even harmonics. The reed can produce both odd and even harmonics, but in the clarinet only the odd harmonics are supported by (line up with) the peaks in the impedance spectrum (above). At high frequencies, the sound harmonics don't often coincide with peaks of impedance, so the difference between odd and even harmonics disappears.
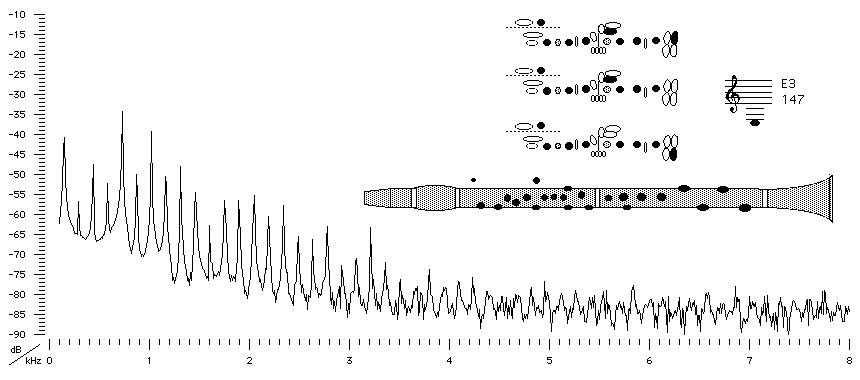
Sound spectrum
of a Bb clarinet
played using fingering for E3
forte .
For more explanation, see
Introduction to clarinet acoustics
For this note (and also for for G4 and A6), we show spectra for different loudness or dynamic levels (f, mp and pp). Note that, as the player blows harder, the level of the fundamental rises somewhat (from pp to mp) but that the fundamental actually becomes weaker from mp to f: the main difference here is that more high harmonics appear and that the harmonics already present become stronger. The more and stronger harmonics change the timbre of the sound, making it brighter or less mellow: listen to the sound files. They are also very effective at making it louder, because our ears are most sensitive in the range 1-4 kHz. (See What is a decibel?) Note also that the base line for all spectra is a broad band 'noise' containing all frequencies. This is due to the turbulence of air passing through the reed opening, and it is an important part of the characteristic clarinet sound, particularly at the beginning of a note.
For a discussion of how the reed motion produces different timbre and dynamic levels, see Playing softly and loudly.
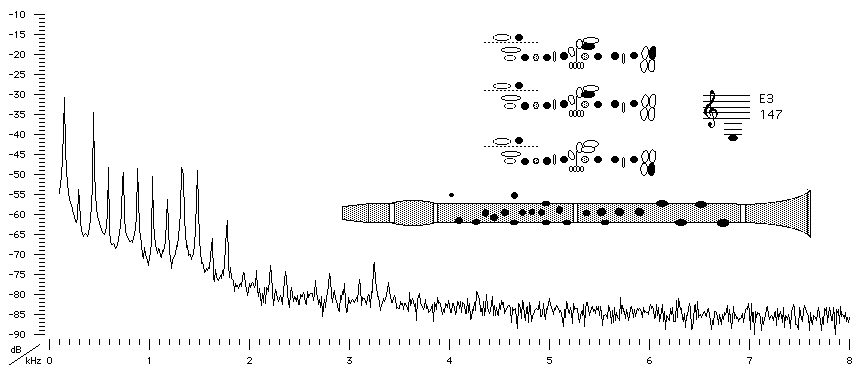
Sound spectrum
of a Bb clarinet played using fingering for E3 mezzopiano.
![]()
![]() You can hear E3 mezzopiano played on a Bb clarinet.
You can hear E3 mezzopiano played on a Bb clarinet.
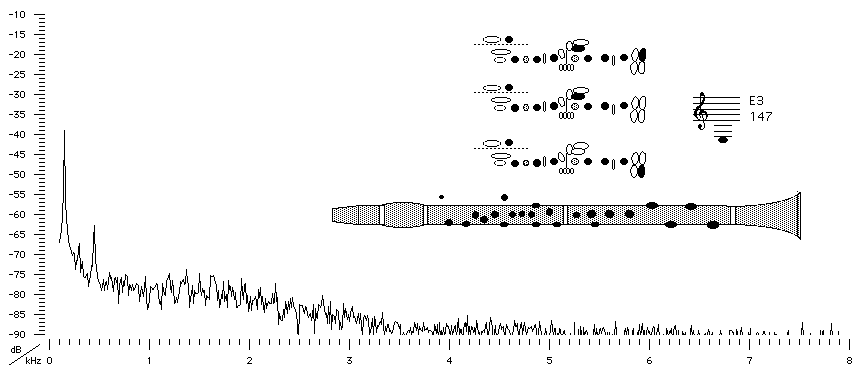
Sound spectrum
of a Bb clarinet played using fingering for E3 pianissimo.
![]()
![]() You can hear E3 pianissimo played on a Bb clarinet.
You can hear E3 pianissimo played on a Bb clarinet.
Contact:
Joe Wolfe / J.Wolfe@unsw.edu.au
phone 61-2-9385 4954 (UT + 10, +11 Oct-Mar)
© 2003 Music Acoustics UNSW